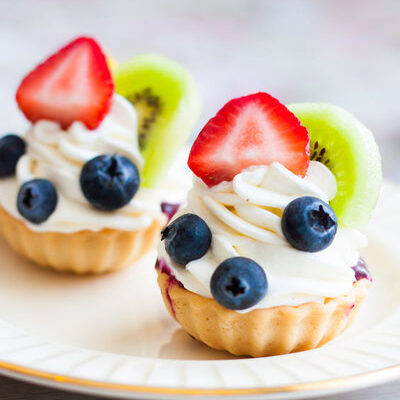

Fruit Tart
What is a Fruit Tart?
A fruit tart is a dish that has a sweet and firm pastry crust, vanilla pastry cream filling, fresh fruits, and a fruit glaze. It is possible to see non fresh fruit toppings on fruit tarts. This dessert has a creamy taste and crunchy texture.
- However, tarts are not the same as pies, even though they look similar.
- The main difference is that tarts only have a bottom crust, which is denser than a pie crust.
According to Taste Atlas, the top 10 most popular tarts in the world are:
- Pastiera
- Pastel de nata
- Egg tart
- Crostata
- Pastafrola
- Pastel de Belem
- Bakewell tart
- Butter tarts
- Treacle tart
- Pastel de feijoa
Origin of fruit tarts
It is believed that the fruit tart came from the idea of the fruit pie. In the 1350s, pies became popular among bakers in Europe. The shortcrust, which differentiates pies from tarts, came into the limelight in the 15th century. Fruit tarts were common in Medieval courts, as they served to beautify the table with their bright, fruity colors. Legend has it that two unmarried French sisters invented the tart, as it is known today, in the 1880s.
The tart was first served in the Hotel Tatin in Lamotte-Beuvron, where the sisters were administrators. In France, the tart’s exact name is known as “Tarte des Demoiselles Tatin” and was served with apples, although it did not become famous immediately. A Parisian restaurant called Maxim’s made the dessert famous after placing it on their menu. While the tart can be made with any fruit, there is a traditional rule that it should be served warm with cream on the side. Tarts were classified into savory and sweet types with the fruit tart falling under the sweet variety. To this day, the apple tart remains the most popular flavor in France.
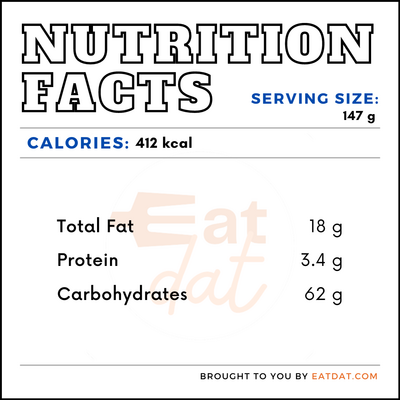
Nutrition
One slice (147g) of fruit tart contains:
Fruit tarts can offer significant health benefits, especially if they contain a lot of fresh fruits. Some benefits include:
- Several fruits contain essential nutrients like folate and vitamin C. Vitamin C helps repair body tissues and folate aids the formation of red blood cells.
- Fruits don’t contain cholesterol. They are also low in calories, which is good for weight loss.
- Many fruits like bananas, prunes, and dried peaches are rich in potassium, which helps maintain blood pressure.
Nonetheless, it is best not to consume this dessert in excess. Fruit tarts contain added sugar and sweet flavored cream. Consuming more than the recommended daily amount of added sugars can cause weight gain and other health issues.
Commercial production
The worldwide fruit and vegetable processing market was valued at $200 billion in 2019. The revenue from the fresh fruit segment of the market was $488,277 million in 2020. This value is expected to rise with a growth rate of 5.4% between 2020 and 2025. The industrial production of tarts involves the use of configurable machines. These machines utilize volume extruders and blocking systems with pneumatic compensation to allow proper dough handling and overall output.
Application
There are vital tips that can help you while making this dessert. Some of them include:
- If you are using salted butter for the tart crust, skip the salt in your recipe.
- It is best to use cold butter for the pastry crust, as it will help make it firmer
- Don’t overwork your pastry dough. This can make the tart crust very tough.
- Use different types of fruits like apples, berries, plums, peaches, and melons.
It is best to eat your fruit tart the same day you made it. Otherwise, you can store it in the fridge for about two days.
Fruit tart recipes
There are several variations of this sweet dessert. Some recipes to try include:
- Fresh Fruity Tart With Vanilla Mascarpone Cream
- Gregg’s Tangy Lemon Tart
- Roasted Cherry Tomato Tart With Herbed Ricotta
- Pineapple Condensed Milk Tart
- French Chocolate Orange Truffle Tart
FDA regulation
Fruits and flavored cream are major ingredients in fruit tarts. The Food and Drug Administration oversees the growing, harvesting, and packing of various kinds of fruits. The organization classifies them as raw agricultural commodities. The body also has standards of identity for multiple types of cream and other related products. Furthermore, the FDA also provides recommended storage conditions for different types of pastry to avoid foodborne illnesses.
References
“The Difference Between Pies and Tarts.” Safeway.ca, Safeway, www.safeway.ca/how-tos/baking-101/pie-differences/.
“Nutrients and Health Benefits.” www.choosemyplate.gov, US Department of Agriculture, www.choosemyplate.gov/eathealthy/fruits/fruits-nutrients-health.
“CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21.” accessdata.fda.gov, US Food & Drug Administration, 1 Apr. 2019, www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=112.1.
