
Cream Cheese
What is a Cream Cheese?
Cream cheese is a dairy product made from cow’s milk and cream, usually in the ratio of 1:2. This type of cheese comes in neutral flavor but can also be infused with a variety of flavors. It is always fresh and never aged. Cream cheese is usually white or cream in color and has a soft and smooth texture like a spread.
- It is most often used as a spread for sandwiches, crackers, bagels, and toast.
- Also, it may be used in certain dishes to add richness, and is a common ingredient in preparing desserts.
The top 8 most popular cream cheese brands are:
- Tillamook
- Belle Chevre
- Gina Marie
- Kite Hill
- Zingerman’s
- Philadelphia
- Miyoko’s
- Green Mountain Farms
Origin of cream cheese
This cheese has its roots in Normandy, France in the 6th century, in the village of Neufchâtel-en-Bray. Known as Neufchâtel cheese, this creamy creation is one of the oldest cheeses made in France. However, this is an aged cheese, while the modern version is much smoother and usually not aged. What we know as cream cheese today came about in 1892 in the US.
It was a happy accident that led William Lawrence to discover this cheese when attempting to recreate Neufchâtel. This new version was marketed under the name of Philadelphia Cream Cheese. In 1960, it began to be marketed outside the US, and quickly became popular throughout the world.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for cream cheese (1 cup, 232g):
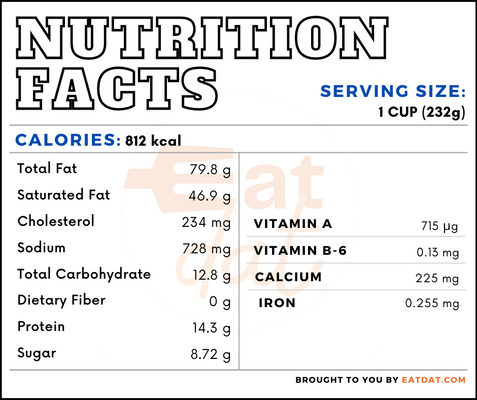
This cheese is rich in potassium, sodium, retinol, and vitamin A. Also, it contains lactose, calcium, magnesium, phosphorous, selenium, folate, choline, carotene, lutein + zeaxanthin, vitamin K, and fatty acids in decent quantities.
Regular consumption of cheese may help in combating inflammation, preventing osteoporosis and arthritis, decreasing the risk of fractures, and managing obesity. The Lactobacillus spp. and Bifidobacterium spp. strains found in cream cheese are useful in preventing Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, it may be useful in the prevention of diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and obesity.
Commercial production
Cream cheese is prepared with a mixture of milk and cream. The proportion of cream in the mixture will determine the creaminess of the end product. First, both ingredients must be pasteurized, and then lactic acid bacteria is added to the mix, allowing it to curdle. Then, the curds and whey begin separating and the curds are then cut once they form a whole mass.
Once cut, the mass is stirred and cooked further until the whey is completely separated, after which it is drained away. Finally, stabilizers are added to the curds, and the product is heated and blended to form the cream cheese. It is packaged fresh and never aged.
Cream cheese recipes
This cheese is mostly used as a spread for sandwiches, bagels, and crackers. However, neutral-flavored cream cheese is often used to enrich desserts. Also, it may be used in pastas, rice, or porridges. Here are a few recipes:
- Cookies
- Lemon Bars
- Cheesecake
- Cheesy Pasta
- Pound Cake
- Brownies
- Grilled Cheese Vegetable Sandwich
- Scrambled Eggs
- American Patriotic Dessert
- Danish Bars
- Dulce de Leche
- Salami Sandwich
- Requeijão
FDA regulations
Cream cheese is defined as a soft, uncured cheese with at least 33 percent milkfat and at most 55 percent moisture, and made using pasteurized dairy ingredients.
References
Beverley Byer, History of Cream Cheese and the Philadelphia Cream Cheese Story, Delishably, https://delishably.com/dairy/History-of-Cream-Cheese-and-the-Philadelphia-Cream-Cheese-Story
Kim, Jong-Hwa et al. “Cream Cheese-Derived Lactococcus chungangensis CAU 28 Modulates the Gut Microbiota and Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis in BALB/c Mice.” Scientific reports vol. 9,1 446. 24 Jan. 2019, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-36864-5, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6345912/
Rozenberg, Serge et al. “Effects of Dairy Products Consumption on Health: Benefits and Beliefs–A Commentary from the Belgian Bone Club and the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases.” Calcified tissue international vol. 98,1 (2016): 1-17. doi:10.1007/s00223-015-0062-x, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4703621/
