
Coconut
What is a Coconut?
Coconut is the fruit of the coconut tree. The name of the fruit comes from the Portuguese word ‘coco’ for skull, referring to the indentations on the shell resembling facial features. It has a green outer covering, under which there is a fibrous brown shell, both of which are inedible. The white flesh and the water contained inside are the edible portions.
Some popular dishes containing coconut are:
- Kaya Toast (Malaysia/Singapore)
- Sopa de Caracol (Honduras)
- Tapado (Guatemala)
- Cazuela de Mariscos (Colombia)
- Coconut Kaukau (Papua New Guinea)
- Laksa (Southeast Asia)
- Rendang (Indonesia)
- Roti Jala (Malaysia)
- Barfi (India)
- Beju (Nigeria)
- Chokladboll (Sweden)
- Coconut Flan (Gabon)
- Haupia (Hawaii)
- Pichi Pichi (Philippines/Palau)
- Quindim (Brazil)
Origin of coconuts
The exact origin of this fruit is unknown. However, there are two different possible origins of this fruit from two different geographical regions, since they show distinct genetic disparity. One group was cultivated in Southeast Asia and the other group in south India, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Archeological evidence shows fossils from New Zealand that date back to 15 million years. Ancient Austronesians carried the fruit to different parts of Asia and Africa through trade. Colonization exposed the Europeans to this fruit who then carried it back with them and to the Americas.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for coconut (1 piece, raw):
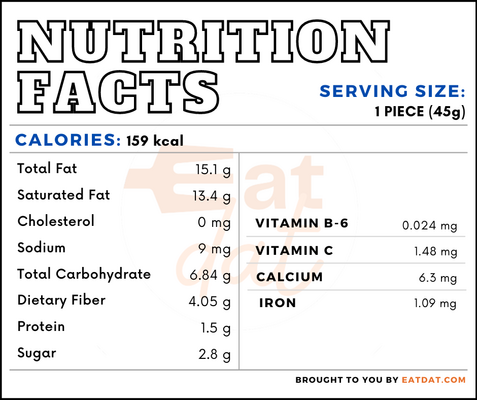
This fruit is rich in potassium. Also, it contains calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, selenium, folate, choline, and fatty acids. Additionally, this fruit has antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiparasitic, and antioxidant properties. Regular consumption of this fruit may help in preventing diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and Alzheimer’s disease. The lauric acid in it promotes brain development, boosts the immune system, and maintains the blood vessels.
Commercial production
The main producers of coconuts are Indonesia, the Philippines, India, Sri Lanka, Brazil, Vietnam, Mexico, and Papua New Guinea.
Coconuts can act as seeds for propagation. This fruit requires a warm climate, high humidity levels, and sufficient rainfall to grow well. It thrives in laterite, alluvial, and red sandy loam soils with decent water holding capacity. They can be harvested throughout the year, and in some orchards, it may be done monthly.
Coconut recipes
This fruit is extensively used in South East Asian, African, Caribbean, and Indian cuisines to prepare different dishes. It may be used to make curries, soups, smoothies, baked goods, desserts, drinks, and even cocktails! Here are a few recipes to try:
- Kuku Paka
- Qumbe
- Avial
- Bharazi
- Mtuzi wa Samaki
- Wali wa Nazi
- Chicken Rendang
- Onde Onde
- Kuih Koci Gula Kelapa
- Ginataang Manok
- Bibingka
- Thengai Sadam
- Beijinho de Coco
- Pol Sambol
- Ika Mata
- Alfajores
- Khow Suey
- Noam Ango’t Skor
- Thai Green Curry
FDA regulations
The FDA considers coconut as a fruit, and any liquid derived from it as a juice. Hence, the milk made from it is classified as a fruit juice in the US.
References
Diana Lutz, Deep history of coconuts decoded, The Source, Washington University in St. Louis, https://source.wustl.edu/2011/06/deep-history-of-coconuts-decoded/
Hewlings, Susan. “Coconuts and Health: Different Chain Lengths of Saturated Fats Require Different Consideration.” Journal of cardiovascular development and disease vol. 7,4 59. 17 Dec. 2020, doi:10.3390/jcdd7040059, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7766932/
Model Profile for 1.0 ha Coconut Cultivation, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development, Department of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, https://agricoop.nic.in/sites/default/files/Coconut%20%281%29.pdf
