
Anchovies
What are Anchovies?
Anchovy is a type of forage fish found exclusively in saltwater. Greenish blue in color, this fish is very small and considered to be an oily fish. Traditionally, it was gutted and salted in brine for preservation and then packed in oil or salt, which led to this fish having a deeply distinct umami flavor. Additionally, anchovy paste, essence, and pickles are available.
- As the fish dissolves when cooked, it can be added to a large variety of savory dishes for flavor.
- It is widely consumed in European and Asian countries.
The top 8 anchovy brands on the market are:
- Agostino Recca
- Bellino
- Cento
- Crown Prince
- Merro
- Ortiz
- Polar
- Roland
Origin of anchovies
This fish is native to the Mediterranean region, and are found in abundance in the Alboran Sea, Aegean Sea, and Black Sea. It was popular in Ancient Rome, and a paste called garum was made from it more than 2,000 years ago. Also, it was believed to be one of the first toppings for pizza when it was originally invented in Naples. In addition, anchovies were popular in Ancient China, where they were made into kchiap, an anchovy sauce from which modern ketchup descended. In a significant event for anchovy fishing, the Peruvian fishery collapsed in 1972 due to overfishing and warming from El Niño, which lasted until 1986.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for anchovies (1 whole, 45g):
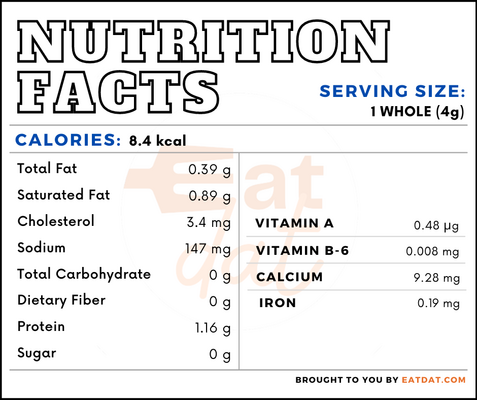
Anchovy is rich in calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and sodium. Also, it contains iron, magnesium, selenium, niacin, folate, choline, vitamin A, retinol, vitamin D, vitamin E, vitamin K, and fatty acids. In addition, anchovies are rich in omega-3 PUFAs, which decrease the risk of coronary heart disease, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, and sudden death.
Commercial production
The anchovies are caught fresh off the ocean in several parts of the world. The preservation process begins immediately within a few hours. First, the fish are spread out and salted. This is done by cutting off the heads and placing them in barrels in layers, salted with sea salt.
Then, the layers are pressed, ensuring that the water and fats are removed. After that, the ensuing product is aged for more than 12 months in the brine. Once the aging is over, the anchovies are cleaned out with fresh water and the scales and crust are removed, as well as the spine, leaving the fish in two halves. Finally, it is dried and packed into containers with olive oil.
Anchovie recipes
This fish can be used as toppings in pizzas, salads, and fillings for sandwiches. They are often used in sauces, marinades, dressings, and dips to impart that umami flavor. Also, they may be added to cooked dishes since they dissolve in heat, leaving behind a rich flavor. Here are a few recipes.
- Spaghetti Puttanesca
- Netholi Niravu
- Balado Teri
- Tumis Oyong Teri
- Fried Rice
- Chan Choy Tong
- Vellyache Hooman
- Nethili Meen Kuzhambu
- Coca de Escalivada
- Tortiera di Alici
- Boquerones Fritos
FDA regulations
Fish is regulated by the FDA. The organization defines fish as any fresh or saltwater finfish, crustaceans, and other forms of aquatic animal life intended for human consumption. Also, the FDA provides food safety recommendations for all types of seafood, including anchovies.
References
Emily Naismith, Food We Fight About: Anchovies, Broadsheet, https://www.broadsheet.com.au/melbourne/food-and-drink/article/food-we-fight-about-anchovies
Climate Variability & Marine Fisheries, PFEL Climate & Marine Fisheries, https://www.pfeg.noaa.gov/research/climatemarine/cmffish/cmffishery4.html
Sidhu, Kirpal S. “Health benefits and potential risks related to consumption of fish or fish oil.” Regulatory toxicology and pharmacology : RTP vol. 38,3 (2003): 336-44. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2003.07.002, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14623484/
