
Almond Flour
What is Almond Flour?
Almond flour is a type of flour made from ground almonds. Blanched almonds are ground to make almond flour, while almonds ground with their skins are known as almond meal. Almond flour is an integral ingredient in some sweet and dessert dishes.
- However, it has also gained popularity as a substitute for wheat flour in recent years due to its health benefits.
- The flour has a strong almond taste with a sweetish nutty flavor that stands out, especially in baked goods like macaroons.
The top 10 almond flour brands are:
- King Arthur Flour
- Anthony’s
- Gluten Free Mama
- Bob’s Red Mill
- Oh Nuts!
- JK Gourmet
- Wellbee’s
- Sincerely Nuts
- Almond Pro
- Now Real Food
Origin of almond flour
Almonds might be one of the first trees to be domesticated. Wild almonds contained high levels of cyanide, making it dangerous for humans. However, a natural mutation occurred at some point, making it safe to eat. Travelers and traders traveling through the Silk Road from Asia to Europe fed on the almonds that were plentiful in Central Asia. Franciscan monks brought the almond tree to the Americas, where it flourished.
Today, almonds are a worldwide crop and are consumed across geographical regions and cultures. Almond flour originated in the Middle East where they were used to prepare a variety of sweets and biscuits. Then, they then spread to Italy and the rest of Europe from where it became widespread in the 16th century through Catherine de Medici. Recently, almond flour has become a popular alternative to wheat flour especially for low-carb, keto, and gluten-free diets.
Nutrition
Nutritional profile for almond flour (1 cup):
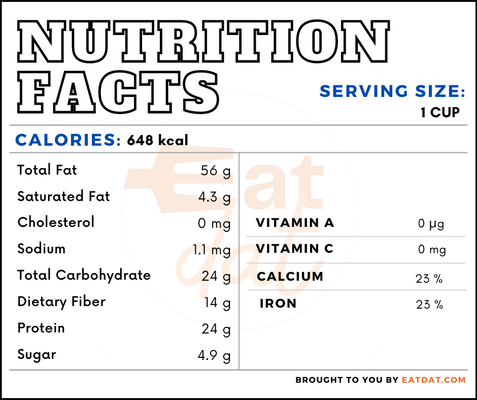
Almonds are high in fat, protein, fiber, calcium, iron, and potassium. Additionally, they are rich in niacin, pantothenic acid, riboflavin, thiamin, vitamin E, vitamin B6, copper, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc. Also, almonds have a low glycemic index, making them perfect for diabetics. Almonds are associated with cardiovascular health and other obesity-related diseases because of their tendency to reduce LDL cholesterol. The nuts have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties due to the polyphenolic compounds in them, such as flavonoids and proanthocyanidins. These are mainly located in the skin of the almonds.
Processing of almonds for producing the flour may lead to some loss of nutrients. Blanching may lead to alteration in cytoplasm and loss of nutrients. Also, nutrients may be lost with particle size reduction.
Commercial production
The USA is the top almond production country in the world, followed by Spain, Iran, Morocco, Syria, Turkey, Italy, Australia, Algeria, and Turkey. Also, the USA is the top almond consumer, followed by India, Germany, and Spain. Almond flour is produced by grinding almonds to powder. It is usually a by-product of almond oil processing.
Almond flour recipes
This flour can be used in a variety of ways. It can be used in both sweet and savory dishes. In addition, it is used to prepare sweets, baked goods, breads, pasta, biscuits, and cakes. Here are a few recipes using almond flour:
- Persian Love Cake
- Baklava
- Toot
- Fufu
- Qumbe
- Kaber Ellouz
- Xiaodianxin
- Ricciarelli
- Financier
- Almond Pasta
- Ghriba
- Pandan Chiffon Cake
- Basbousa
- Marzipan
- Muhammara Dip
- Borek
- Mucver
- Tarta de Santiago
- Almond Barfi
FDA regulations
The FDA regulates almonds as a tree nut and has specific regulations regarding the packaging. Almond flour falls under the milled grain products category.
References
Artem Milinchuk, A Brief History of Almonds, Farm Together, https://blog.farmtogether.com/a-brief-history-of-almonds
Almond Flour Market – Global Industry Analysis, Size, Share, Growth, Trends and Forecast 2018 – 2026 Food & Beverages TMRGL57717 Ongoing Jan 2022, Transparency Market Research, https://www.transparencymarketresearch.com/almond-flour-market.html
Liu, Yanan et al. “The effects of daily intake timing of almond on the body composition and blood lipid profile of healthy adults.” Nutrition research and practice vol. 11,6 (2017): 479-486. doi:10.4162/nrp.2017.11.6.479, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5712498/
Barreca, Davide et al. “Almonds (Prunus Dulcis Mill. D. A. Webb): A Source of Nutrients and Health-Promoting Compounds.” Nutrients vol. 12,3 672. 1 Mar. 2020, doi:10.3390/nu12030672, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146189/
