
Unpasteurized Milk
What is Unpasteurized Milk?
Unpasteurized milk, also known as raw milk, is milk that is not treated for bacteria. Pasteurization is a process that consists of heating milk to kill off the harmful germs that develop soon after it is milked from the cow or another animal.
- Raw milk is milk that does not undergo this process and is instead sold fresh.
- Proponents of the raw milk movement claim that pasteurization destroys the beneficial proteins and enzymes that can boost the immune system.
Another reason is that they believe this milk is full of healthy bacteria, which gets destroyed by pasteurization.
Some popular raw milk brands include:
- Claravale Raw Milk
- Organic Pastures
- SideHill Farm Certified Organic Raw Milk
Origin of unpasteurized milk
When humans began to consume milk, it was raw. The first animal to be milked for human consumption was the now-extinct aurochs, around 8,000 to 10,000 years ago, probably in Central or Northern Europe. It is now believed that milk-drinking became common under famine conditions when nothing else was available. Pasteurization, invented by French scientist Louis Pasteur in the 1860s, made milk safer for most people to consume and decreased the number of milk-related diseases. However, raw milk is still popular in most rural areas around the world, where the production to consumption time frame is very short.
Nutrition
The nutritional value for one glass of raw milk:
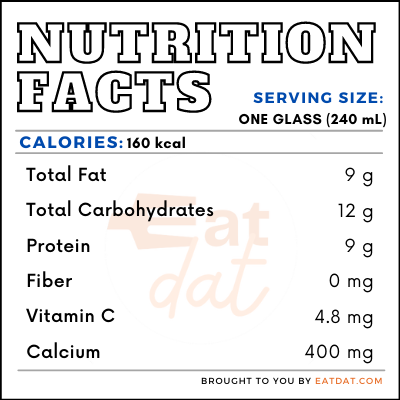
Proponents of raw milk believe that it offers certain benefits, such as controlling asthma development, as well as helping use calcium and antioxidants more effectively. Heating unpasteurized milk destroys the B vitamins and vitamin C that is so useful in this beverage. However, the FDA offers a rebuttal to these theories in its review. Despite this, some studies have shown that consuming raw milk may reduce the risk of respiratory infection, fever, asthma, and atopic dermatitis.
The pathogens in unpasteurized milk are the result of fecal matter getting into the milk. Raw milk contains a number of harmful bacteria and pathogens such as E. coli O157: H7, Salmonella, Streptococcus spp. Yersinia enterocolitica, Campylobacter jejuni, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Coxiella burnetii, etc. These bacteria can cause serious illnesses such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, tuberculosis, and can even lead to death.
Commercial production
Unpasteurized milk is milked from cows and other animals and is sold without heat processing to end customers. Most raw milk is sold on farms and comes from grass-fed cows. New systems have been built to teach farmers how to handle fresh milk, maintain cow hygiene, and increase hygiene during the milking process. These regulations are used to avoid infecting the cows and milk to prevent raw milk-based diseases.
Unpasteurized milk recipes
This milk can be used just like pasteurized milk. Here are a few popular recipes:
- Raw Butter
- Raw Milk Yogurt
- Raw Milk Cottage Cheese
- Ice Cream
- Raw Mozzarella Cheese
- Sour Cream from Raw Milk
- Clabber Cheese
- Raw Whipped Cream
FDA regulations
The FDA prohibits the sale of unpasteurized milk across state borders. A farm can only sell its raw milk produce locally. Import of unpasteurized milk into the US is also strictly regulated and a number of tests must be conducted before import. The USDA conducts grading of raw milk and unpasteurized milk products and also sets guidelines for its packaging, storage, and testing.
References
“Raw (Unpasteurized) Milk.” Cdc.gov, Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 22 Jan. 2020, www.cdc.gov/features/rawmilk/index.html.
“The Raw Milk Movement: Healthy or Hazardous?” Realmilk.com, A Campaign for Real Milk, 5 Feb. 2014, www.realmilk.com/safety/raw-milk-movement-healthy-or-hazardous/.
Berge, A C, and T Baars. “Raw milk producers with high levels of hygiene and safety.” Epidemiology and infection vol. 148 e14. 31 Jan. 2020, doi:10.1017/S0950268820000060, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7019599/
Raw (Unpasteurized) Milk, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, https://www.cdc.gov/features/rawmilk/index.html
Raw Milk Misconceptions and the Danger of Raw Milk Consumption, US Food & Drug Administration, https://www.fda.gov/food/buy-store-serve-safe-food/raw-milk-misconceptions-and-danger-raw-milk-consumption
