
Elderberry Wine
What is Elderberry Wine?
Elderberry wine is an alcoholic beverage produced from the fermentation of elderberries and other ingredients. The scientific name for the elderberry plant is Sambucus nigra and it belongs to the honeysuckle family (Caprifoliaceae). Elderberries have colors that range from dark purple to black.
- This drink has a unique flavor that changes over time.
- Elderberry wine is commonly produced at home, although there are a few commercial brands which sell it.
The most common elderberry cultivars include:
- Beauty
- Black Lace
- Adams #1
- Adams #2
- Johns
- Nova
- Variegated
- Scotia
- York
Origin of elderberry wine
Elderberry is a fruit that has always been present in folk medicine with its remains being found in Stone Age communities. During the middle ages, people considered the elderberry as a Holy Tree capable of maintaining good health. Hippocrates called this berry “nature’s medicine chest.” All the parts of this plant have played different roles in treating various health conditions. The production of this homemade fruit wine was a source of interest for many people, as it was seen as a less expensive option than imported wines.
Function
Aside from making wine, various parts of the elderberry plant can be used for other things. Elderberry syrup can be used as a flavor in smoothies and gummies. Also, elderberries can serve as an ingredient in baked goods like pancakes, muffins, and pies. The flower of this plant can be used in salads and elderberry tea. Additionally, the juice from this berry helps relieve pain from burns when made into a salve.
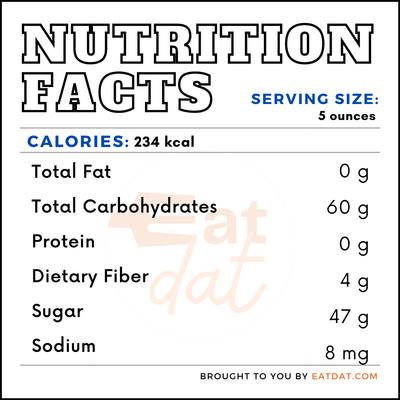
Nutrition
A 5 oz serving of elderberry wine contains:
The elderberry is the main ingredient in this wine. This component can be instrumental for healthy bodily functions. Some of the health benefits of this wine include:
- It contains antioxidants that can prevent oxidative stress, reducing the risk of cancer and type 2 diabetes in the long run.
- Elderberries are good sources of phenolic acid and vitamin C.
- It is capable of managing the symptoms of cold, flu, and influenza.
- This drink may encourage proper heart functioning and decreasing fat in the blood.
This fruit wine might not be suitable for children and young people below the age of 18, as well as pregnant women. There is not enough data to certify that elderberries are safe for these groups of individuals. Unripe elderberries and seeds can also cause stomach upset, if consumed in excess.
Commercial production
The large-scale production of elderberry wine starts with separating the berries from their stems and packing them into plastic bags. The next stage is to freeze and store them at -4°F. Later, the berries will be defrosted and processed into wine.
It has been estimated that the worldwide elderberry market size will increase by $188.17 million between 2018 and 2022. The global wine consumption amount dropped from 246 million hectoliters in 2018 to 244 million hectoliters in 2017.
Application
A basic form of elderberry wine is easy to make at home. Simply follow the steps below:
- First, separate the berries from their stems with a fork.
- Then, mash the berries in a pot.
- Next, add water to the mashed berries and boil. Allow the pot’s contents to simmer for 15 minutes to half an hour.
- Then, let the berries cool and add more water to them.
- After that, add lemon juice, nutriment, and a sachet of red wine yeast to the berries to allow fermentation for 4-5 days.
- Finally, strain the berries to get the wine.
Elderberry wine recipes
These fruits can craft a variety of foods and drinks. Some popular recipes include:
FDA regulation
The Food and Drug Administration does not have any regulations concerning elderberry wine. However, the organization has calculated the labeled percentage of elderberry juice from its beverage or concentrate using Brix levels. The minimum Brix level for 100% elderberry juice is 5.7. The FDA requires wines to be bottled, packaged, and labeled according to regulations from the Secretary of the Treasury. However, it is the Alcohol, Tobacco Tax, and Trade Bureau (TTB) that is in charge of inspecting and enforcing these regulations.
References
“Elderberry Wine: Taming the Wild Elderberry.” WineMakerMag.com, WineMakerMag, winemakermag.com/article/841-elderberry-wine.
Mandl, Elise. “Elderberry: Benefits and Dangers.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 8 Mar. 2018, www.healthline.com/nutrition/elderberry.
“CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21.” Accessdata.fda.gov, US Food & Drug Administration, 1 Apr. 2019, www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=101.30.
