
Pine Nuts
What are Pine Nuts?
Pine nuts (Pinus gerardiana) are edible seeds from pinyon pine trees. Up to 20 species of pine produce seeds that are large enough to be harvested. These nuts have been used for food in Asia, Europe, and the United States.
The top five most common types include:
- Chinese white pine
- Siberian pine
- Chilgoza pine
- Korean pine
- Swiss pine
Origin of pine nuts
Pine nuts originated over 10,000 years ago and were a staple in the diet of the indigenous people of the Great Basin. The Shoshone, Hopi, Washo, and Paiutes, and their ancestors ate these seeds as a storable, primary, and multi-faceted food. This nut was relatively challenging to harvest until the region’s people learned how to harvest it just before it reached the final ripening stage. Harvesting these seeds was a defining moment for these people every year and was the most significant gathering in the concentrated areas of the sacred lowland pinyon forest. Today, countries around the world enjoy this soft and flavorful nut in their cuisines.
Nutrition
In a 28g (1 ounce) serving of pine nuts, there are:
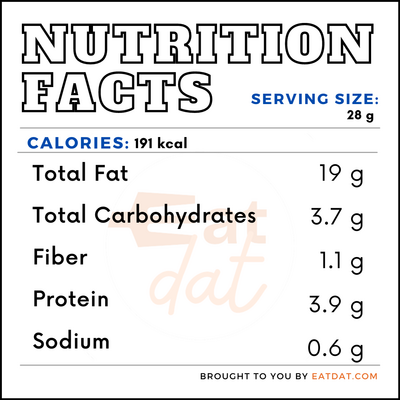
These nuts have several health benefits as they provide an excellent balance of fiber, protein, and fats, which stabilize blood sugar levels. They also offer some cardiovascular benefits that may help prevent stroke and heart attacks. Consuming three servings or more of these nuts per week significantly lowers the risk of atrial fibrillation and heart failure. However, people who are allergic to tree nuts may have to avoid consuming this nut. Oil made from this nut may also pose a severe threat to patients suffering from seizures.
Commercial production
The large-scale production of this nut starts with harvesting the seeds from pine trees. Harvesting these nuts is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, which involves:
- Putting pine cones into a burlap bag
- Leaving the burlap bag in the sun to dry for ten days.
- Smashing the cones and removing the seeds
- Separating the seeds from the cones by hand.
- Manually removing the second shells before they are ready for consumption.
The U.S. market for these nuts is up to $100 million in annual sales, though it is still largely underdeveloped. These seeds are specialty products and are only available via specialized distributors, such as health food stores and catalogs.
Application
These nuts can be toasted or frozen. When frozen, they last for several months, while the oil-rich toasted nuts should be used within two weeks. This is to prevent the natural oil from turning rancid, thus ruining the flavor of these seeds.
Pine nut recipes
These nuts can be used in a variety of dishes. Here are some popular recipes:
- Pesto Pasta Salad
- Basil Pesto Hummus
- Spinach and Pine Nuts
- Syrup-soaked Pastries with Hazelnuts, Pistachios, and Pine Nuts
- Galayet Banadoura (Sautéed Tomatoes with Pine Nuts)
FDA Regulation
The Food and Drug Administration strictly regulates the cultivation, harvesting, and packaging of these nuts. In the past, the agency has issued a strong warning against the consumption of Turkish pine nuts. In 2011, it was suspect that these imported nuts may have been responsible for 43 salmonella illnesses in the United States. This warning came from an outbreak investigation report released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
References
Spengler, T. “Pine Nut Harvesting.” Gardening Know How, 24, Apr. 2020, https://www.gardeningknowhow.com/edible/nut-trees/pine-nut/pine-nut-harvesting.htm.
Frey, Malia. “Pine Nut Nutrition Facts and Health Benefits.” Verywell Fit, 2 Nov. 2020, www.verywellfit.com/pine-nut-nutrition-facts-4586648.
Rothschild, Mary. “FDA Issues Warning on Pine Nuts.” Food Safety News, 29 Oct. 2011, www.foodsafetynews.com/2011/10/fda-issues-warning-on-pine-nuts/.
Bonnie L. Grant. “Where Do Pine Nuts Come From: Learn About Growing Pine Nut Trees.” Gardening Know How, https://www.gardeningknowhow.com/edible/nut-trees/pine-nut/growing-pine-nut-trees.htm
CFR – Code of Federal Regulations Title 21.” Accessdata.fda.gov, U.S Food & Drug Administration, 1 Apr. 2020, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=112.1&SearchTerm=pine%20nuts
