
Lime
What is a Lime?
A lime (Citrus aurantiifolia) is a round, green acidic fruit with a hard peel and soft fleshy interior. This fruit belongs to the Citrus family. Generally, this fruit possesses a diameter that falls between 1 and 2 inches.
Ten common types of lime include:
- Mexican
- Bearss
- Tahiti
- Kaffir
- Calamansi
- Finger
- Blood
- Rangpur
- Limequat
- Omani dried
Origin of lime
This citrus fruit is believed to have originated in Northern India and Northern Malaysia. The Arabs later brought the sour lime into North Africa, Spain, and Portugal. European crusaders from Palestine spread this fruit to the other Mediterranean nations. This fruit was cultivated and became widespread in Italy and France during the mid-1300s. European explorers also brought this citrus fruit to the Americas during the early 16th century.
When this fruit found its way into the United States, it became particularly popular in Florida. Many people even planted trees in their yards. The name “key lime” comes from the Florida Keys. The cultivation of this citrus fruit in Florida increased when pineapple production stopped due to soil depletion and the 1906 hurricane. Today, this citrus fruit remains popular across the globe.
Function
Lime zest and peels can serve as garnish for dishes and drinks. In the kitchen, this fruit also gives an excellent flavor to desserts and baked goods. Not to mention that lime juice serves as a powerful flavoring agent for sauces, salads, meat, fish, and a variety of other foods.
Nutrition
A serving size of 100g of raw lime juice contains:
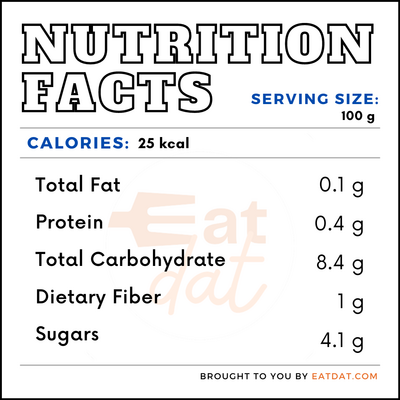
This fruit has several health benefits, including:
- It is acidic and can break down food to aid better digestion.
- It can increase the metabolism, burn calories, and assist in weight loss.
- This fruit can reduce the risk of heart disease or stroke.
- It can relieve inflammation in the body.
- The vitamins in this fruit can help to boost the immune system.
There are some risks associated with limes, mainly with the bacteria from their peels. It’s vital to wash the fruit properly before using it. If you are planning to use its zest, opt for an organic product when possible.
Commercial production
Loamy soil and sandy soil are the best for this fruit. The pH range for optimal fruit yield is 6.0 to 6.5. A slope of fifteen degrees would be ideal for minimizing the risk of erosion. Generally, citrus trees can withstand high temperatures, provided that there is adequate soil moisture.
In 2019, China, the United States, and India were the world’s top three producers of this fruit. The worldwide market value for limes in 2019 was valued at $47 billion. This value is expected to hit $59.5 billion by 2025, with a growth rate of 4% between 2020 and 2025.
Application
Before you store these citrus fruits, make sure that you wash them. First, wash your hands with warm soapy water. Then, use clean tap water to wash the limes. Use a clean towel to clean the fruits before refrigerating them.
The best way to store limes is to place them in a ziplock bag and put them in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator. This way, they will last for about six weeks. If you notice any signs of mold on any of the fruits, throw them away immediately because it can damage the other fruits. When purchasing this fruit, select the ones that are fresh and blemish-free, with no sign of breakage on the skin.
Lime recipes
This citrus fruit can be used in countless dishes and drinks. Here are some top-rated recipes:
- Super Easy Lime Bars
- Honey, Ginger, Lime, Rum Glazed Shrimp
- Grilled Salmon Tacos With Chipotle Lime Yogurt
- Vietnamese Beef Pho
- Thai Beef Cabbage Cups
FDA regulation
The Food and Drug Administration classifies lime as a raw agricultural commodity. The FDA controls the growing, harvesting, and packing of this citrus fruit. They also consider this food one of the top 20 most frequently consumed raw fruits in the United States.
References
Megan, Ware. “Limes: Nutrition, Benefits, and Diet.” Medical News Today, MediLexicon International, 26 Feb. 2018, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/304448.
“CFR – Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21.” accessdata.fda.gov, US Food and Drug Administration, 1 Apr. 2019, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=112.1&SearchTerm=lime
