
Brussels Sprouts
What are Brussels Sprouts?
Brussels sprouts are a member of the Brassica oleracea family of cruciferous vegetables, which also includes cabbage, cauliflower, and kale. They look like tiny cabbages and have the same pale green color. Brussels sprouts have a bitter, yet sweet and nutty taste. The bitterness is due to a sulfur-containing phytochemicals, glucosinolate, which also gives this vegetable its distinctive odor.
- Brussels sprouts come in several different varieties, the main ones being Early Half Tall, Bedford, and Noisette.
- Other varieties include Peer Gynt, Welland, Citadel, Rampart, Fortress, and Zid Fasolt.
Here are some common ways to prepare Brussels sprout:
- Roasted
- Steamed
- Chopped
- Veggie Kebab
- Blanched and added to salad
- Stir Fry
- Steamed and coated in marinade
- Candied
- Smoothies
Origin of Brussels sprouts
Native to the Mediterranean region, these vegetables most likely originated in Italy. Studies suggest that they may have mutated from wild cabbage. This vegetable’s name comes from the fact that Brussels sprout was a huge crop in the 16th century in Brussels, Belgium. French colonists would later take this vegetable to the US around the year 1800.
Nutrition
Brussels sprouts are a nutritious food that is high in vitamins A, C, and K, as well as folate and manganese. This vegetable scores high on the Aggregate Nutrient Density Index score, which measures vitamin, mineral, and phytonutrient contents in relation to calories. A 100-g serving contains:
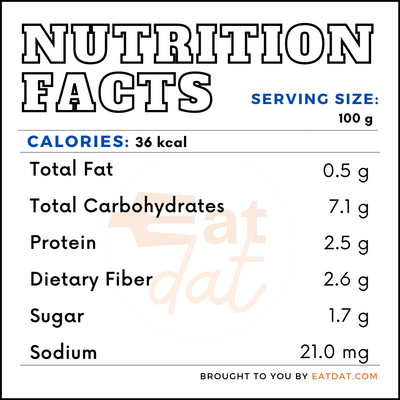
This vegetable can have cancer-prevention properties because of the presence of glucosinolates, isothiocyanates, and indoles. The chlorophyll in them also has cancer-prevention properties. Other research has also shown that this vegetable may protect from oxidative stress, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
However, people with thyroid problems should refrain from overconsuming Brussels sprout. Due to the high progoitrin concentrations, they can decrease iodine uptake into the thyroid, thus affecting the production of the thyroid hormone.
Commercial production
Brussels sprout requires cool weather and well-drained, loamy soil. Harvesting them involves picking or cutting the buds off the stem when they are firm and before the leaves turn yellow. The vegetables are often stored at 32 °F (0°C) and kept moist for best preservation. Under optimum conditions, they can remain fresh for a period of 4 to 6 weeks.
The main Brussels sprout producing countries are China, Russia, India, Korea, and Japan. The main exporters are the Netherlands, Mexico, the USA, Belgium, and Morocco.
Brussels sprouts recipes
These vegetables are a healthy addition to any meal. Here are a few popular recipes:
- Garlic Roasted Brussels Sprout
- Sesame Brussels Sprout Soba Bowl
- Brussels Sprout & Cashew Fried Rice
- Garlic Roasted Salmon & Brussels Sprout
- Brussels Sprout Soup
- Brussels Sprout & Gruyere Quiche
- Brussels Sprout, Mushroom, and Bleu Cheese Pie
- Brussels Sprout Curry
- Brussels Sprout Paruppu Usili
- Cowboy Steaks & Brussels Sprout
FDA regulations
The FDA describes all fresh vegetables, including Brussels sprout, as raw agricultural commodities and strictly regulates all aspects of their growing, harvesting, packing, and storage. Canned Brussels sprout also fall under the purview of the FDA. The USDA regulates the grades of these vegetables and specifies that their diameter must not exceed one inch and their lengths are no longer than 2-3/4 inches.
References
“Brussels Sprout.” Frutas-Hortalizas.come, Interempresas Media, S.L., www.frutas-hortalizas.com/Vegetables/Types-varieties-Brussels-sprouts.html.
Brussels Sprouts, The Nutrition Source, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/food-features/brussels-sprouts/
Hwang, Eun-Sun. “Influence of Cooking Methods on Bioactive Compound Content and Antioxidant Activity of Brussels Sprouts.” Preventive nutrition and food science vol. 22,4 (2017): 353-358. doi:10.3746/pnf.2017.22.4.353
