
Nut Milk
What is Nut Milk?
Nut milk is a creamy beverage made from any type of nut. This non-dairy milk is becoming increasingly popular as a replacement for cow’s milk. Nut milk is often used in the same ways as cow’s milk for baking and cooking.
- However, some of these kinds of milk can also be used to prepare different types of desserts, main dishes, and beverages.
- This milk may also be sweetened or unsweetened.
The most common types of nut milk are:
- Almond
- Cashew
- Hazelnut
- Macadamia
- Walnut
- Pistachio
- Coconut
- Peanut
Origin of nut milk
Though cow’s milk (and other animal milk) have been consumed for centuries, the first mention of any type of nut milk is more recent. In the 13th century, almond milk was featured in a recipe book in Baghdad. Later on, in the 14th century, Egyptian and English recipe books also mentioned almond milk. However, coconut milk is thought to be older, with different Asian cultures using it as far back as 2,000 years ago. Today, there are multiple varieties of nut milk available all over the world.
Commercial production
Some people make this milk at home, although the demand for commercial nut milk is high. The commercial production process involves first harvesting and selecting nuts for quality, then they are then either wet or dry processed. The wet processing method involves soaking the nuts in water and salt and then grinding to a paste. Dry processing involves drying the nuts and then grinding them into flour.
Next, water, thickeners, and stabilizers are added to the paste or flour to prepare the beverage. The milk is then enriched with vitamins and minerals before thermal processing or pasteurization is completed. This is then packaged and sent out for distribution. However, different nuts may have minor differences in their production.
While this type of milk is often consumed as a healthier and more ecological alternative to dairy milk, almond milk has recently run into ethical issues. Recent research has shown that the American almond industry led to the deaths of almost 50 billion bees in a single year. Coconut milk also has led to the destruction of rainforests in some areas.
Nutrition
One cup (8oz) of almond milk contains:
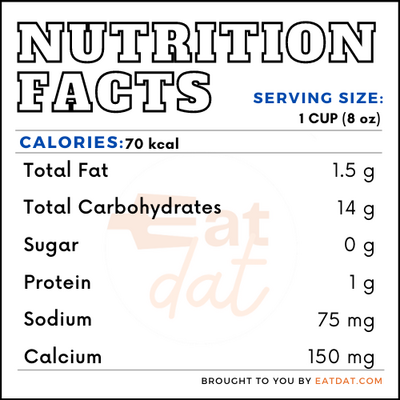
Nut milk is a great alternative for lactose-intolerant people. Although they don’t have the calcium and protein content of cow’s milk, this milk have a host of other vitamins and minerals to make up for it. Not to mention that these milk generally have fewer carbohydrates. However, some of these milk may also be allergenic, such as peanut milk.
The micronutrients depend on the ingredients they contain. For instance, almond milk has good amounts of calcium, as well as vitamins B12 and D. Coconut milk has healthy fats, calcium, and vitamin D. Cashew milk contains protein and is often enriched with calcium and vitamin D. Whereas, hazelnut milk is rich in vitamins A, E, and D, as well as calcium and protein.
Nut milk recipes
This is versatile and lends itself to any number of dishes. Here are a few popular recipes:
- Peanut Milk Ice Cream
- Cauliflower Coconut Curry
- Almond Milk Pancakes
- Keto Dosa
- Cashew Alfredo Pasta
- Chocolate Hazelnut Cake
- Hazelnut Hot Chocolate
FDA regulations
The Food & Drug Administration does not classify this type of milk as ‘milk’, since only the lacteal secretion of cows, which is free of colostrum, can be labeled as such. Serious attempts have been made by the FDA to rule out any non-dairy products as milk, which has left alternative milk products, including nut milk, undefined and unclear. Nuts, or tree nuts, are graded and standardized by the USDA, which specifies the quality of the nut product. The provisions for this include all the different nuts mentioned above.
References
Veronika Powell, A brief history of plant milks, Viva!Health, https://www.veganfoodandliving.com/features/a-brief-history-of-plant-milks
Benjamin Kemper, Nut Milks Are Milk, Says Almost Every Culture Across the Globe, Smithsonian Magazine, https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/nut-milks-are-milk-says-almost-every-culture-across-globe-180970008/
The History of Nuts, Nutcracker Museum, http://www.nutcrackermuseum.com/history_nuts.htm
Ros, Emilio. “Health benefits of nut consumption.” Nutrients vol. 2,7 (2010): 652-82. doi:10.3390/nu2070652, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257681/
