
Onion
What is an Onion?
The onion is a member of the Allium family of vegetables and comes in different sizes, shapes, and colors. The most prominent types of this vegetable are yellow, white, and red.
- This vegetable commonly releases vapors when being chopped, which causes sometimes painful watery eyes.
- Nonetheless, this vegetable is almost indispensable in the kitchen.
In 2018, the U.S. estimated production value of utilized onions was $817.5 million.
Some common ways to use onions in the kitchen include:
- Frying
- Roasting
- Pickling
- Grilling
- Garnish
- Salad
- Adding flavor to soups and sauces
Origin of onions
Onions most likely originated in Central Asia, although records don’t indicate the precise time and location of the cultivation of this plant. This is likely because of the perishable nature of this vegetable. Researchers speculate that this plant may have first grown in Central Asia, while others insist on the Middle East, specifically in West Pakistan and Iran. Nonetheless, many believe that the planting of this vegetable began long ago, before writing and the production of sophisticated tools. Organized cultivation of this vegetable later began around 3,500 BC.
Ancient peoples loved to dry and preserve this plant for periods of famine, as this vegetable could prevent thirst and had several valuable medicinal benefits. This vegetable also held an essential place in the heart of Egyptian meals, ceremonies, and religious events. The popularity of this plant grew in the early years of AD with Greek physicians using it heavily. The Romans ate a lot of this vegetable and spread it to most of Central Europe and England, where it was popular during the Dark and Middle Ages. Today, this plant continues to be widely produced and used in a variety of dishes.
Nutrition
In a serving size of 100g of onions, there are:
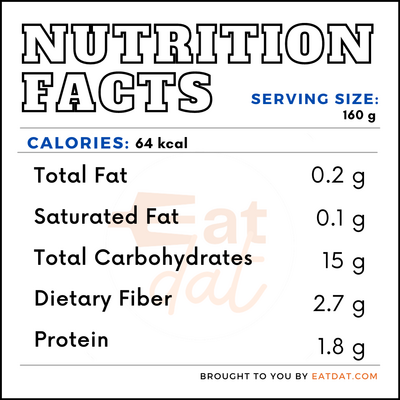
This vegetable has numerous health benefits. Here are some of them:
- It is rich in vitamin C, which helps to maintain immune health.
- It has anti-inflammatory properties that can lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- They are rich in fiber, which is good for the digestive system.
- Consumption of this vegetable has been linked to stable blood sugar levels.
However, this nutritious vegetable also has side effects:
- If eating it increases your indigestion symptoms, then reduce your consumption.
- It may slow blood clotting and increase the risk of bleeding after surgery.
Commercial production
Onion seeds or bulbs require a minimum temperature of 50°F to grow. The best location for growing this plant is where it will have full sun exposure. The soil for planting this vegetable should be loose, adequately drained, and rich in nitrogen. Aged manure is also added to the land because onion plants need constant nutrients. Fertilizer application is another essential factor in ensuring proper growth. This plant requires crop rotation to prevent the spread of diseases and guarantee a healthy harvest.
Application
The best place to store onions is a cool, dry, and adequately aerated place, as they absorb moisture quickly. High temperatures or humidity can also make them rot. Place this plant in an open basket or mesh bag to ensure proper air circulation, since inadequate ventilation will damage them.
Avoid placing this vegetable in plastic bags. Additionally, avoid storing whole, unpeeled onions in the fridge because they will absorb moisture and rot faster. Sliced and peeled onions can stay in the refrigerator for between 7-14 days. When cooked, this vegetable can remain in the fridge for 3-5 days.
Onion recipes
This vegetable is a popular ingredient in cooking and can be prepared in many ways. Here are some recipes to try:
- Easy cheese and onion slice
- Sausage, sage & onion stuffing
- Cheeseboard & onion tart
- Caramelized carrots & onions
- Quick pickled onions
FDA regulation
The Food and Drug Administration classifies onion as a raw agricultural product and monitors every aspect of its cultivation, growing, and harvesting. The FDA also has a standard of identity for canned onions, which they define as a vegetable ingredient obtained by proper preparation of the succulent bulb of this vegetable plant. Optional ingredients like spice, refined sugar, and mint leaves are allowed in canned onions. The FDA’s guidelines also state rules concerning the processing, packaging, and labeling of this canned vegetable.
References
Raman, Ryan. “The Best Way to Store Onions.” healthline.com, Healthline Media, 17 May 2018, www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-to-store-onions.
Megan, Ware. “Onions: Benefits and Nutrition.” medicalnewstoday.com, MediLexicon International, 15 Nov. 2019, http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/276714
“CFR – Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21.” accessdata.fda.gov, U.S. Food & Drug Administration, 1 Apr. 2019, www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=155.200.
